ESLint Rules
Modern.js ESLint Rules is the full set of ESLint rules, includes @modern-js (Lint rules for Node.js projects) and @modern-js-app (Lint rules for web projects).
More ESLint usage is described below with specific questions.
Q: How To Deal With Lint
Automatic Fix
Most problems will be solved by the automatic fix of ESLint rules or the code formatting of Prettier (which has been integrated into ESLint), and the developer does not need to care about the details of the problem and how to solve it.
This kind of automatic fix is mainly performed when the IDE saves the file, and a few will be automatically fix on submit.
Batch Automatic Fix
In rare cases, such as when an old project is migrated, the following commands can be executed to repair and inspect all files in bulk:
Manual Fix
For problems that cannot be automatically fixed, you can click the rule link in the problem prompt box in the IDE to open the document of this rule to view the explanation and solution of the problem.
Claim Exceptions
At this stage, some rules are not smart enough, and in most cases there will be great benefits, and in a few cases it may not apply. But if the entire rule is turned off or changed for these few cases, the gain is not worth the loss.
In this case, you can use the eslint-disable comment to mark the code blocks that meet the rare case, stating that this is an exception and should be ignored. For example:
Enter eslint in the VS Code editor, a prompt box about eslint-disable will automatically appear, select the prompt option to generate the corresponding comment pair.
[Modern.js ESLint Rule Set] requires that eslint-disable must be used in pairs, the scope to be affected must be clearly expressed, and what rules to disable within this scope must be clearly expressed, the purpose is to make exceptions Clear, minimized scope to avoid abuse of eslint-disable, resulting in code that does not belong to the exception being disabled by the rule.
Q: How to customize ESLint rules
The eslintConfig field in package.json in the root directory
This place is the default ESLint configuration for the entire repository and is designed for pure Node.js code (which can only run in Node.js).
If the project does have special requirements or inevitable compatibility issues with some rules (not exceptions), you can add rule configuration here. This configuration will take precedence over the default [Modern.js ESLint ruleset], such as:
src/.eslintrc.js
Modern.js Framework or Modern.js Module project will have this configuration file by default in the source code directory, which is designed for Universal JS code.
Universal JS code is code that can run on both the browser side and the server side.
If the project does have special requirements or inevitable compatibility issues with some rules (not exceptions), you can add a rule configuration here, which will take precedence over the default [Modern.js ESLint ruleset], such as:
If necessary, you can continue to add the .eslintrc.js file in different subdirectories, and make special configuration for the code in this subdirectory:
Note: It is not necessary to use the extends field, it will automatically inherit the configuration of the parent directory.
eslintIgnore field in package.json
Adding directories that contain .js, .jsx, .ts, .tsx files, but do not require code inspection and automatic repair, to eslintIgnore can optimize the speed of ESLint inspection, such as:
Q: How to upgrade the version of the ESLint plugin
As long as it is not a change in the Major version (the "^" symbol that does not comply with the Semver rule), you can specify this dependency directly in the package.json of the business project, delete the Lock file (or try to manually delete the Lock file). the contents of this package name in the file), execute pnpm install to reinstall the dependency and generate a new Lock file.
After doing this, the plugin should only exist in the ./node_modules directory of the business project and be upgraded to the version you specified.
- Major version is the major version number. For more information, please read [Semantic Versioning ].
- All upstream projects encapsulated by Modern.js (such as ESLint, ESLint plugin, React Router, etc.) can also be upgraded in this way.
- Modern.js will also try to upgrade these upstream dependencies as timely as possible in each release.
- Major version upgrades need to be published by Modern.js.
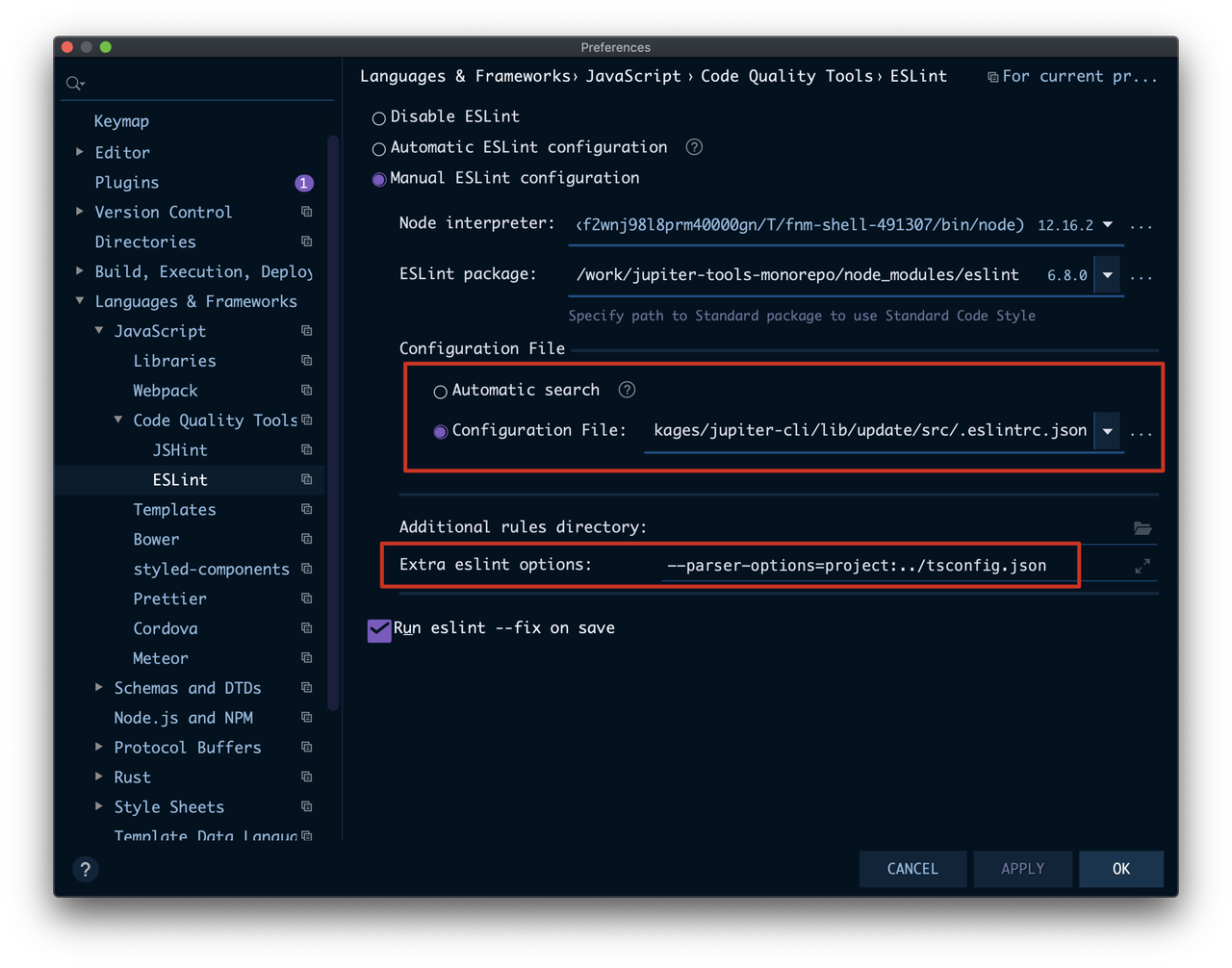
Q: WebStorm sometimes reports ESLint errors
Since WebStorm believes that the ESLint execution directory is determined based on the .eslintrc' file. Therefore, the placement of the src/.eslintrc file location will cause the location specified by the tsconfig.json file (in the project root directory) to not be found in the'src/'directory.
you need to configure it manually: