HMR FAQ
How to troubleshooting HMR ineffective issues?
There are several possible reasons why HMR may not be work. This document will cover most common causes and provide guidance for troubleshooting. Please refer to the following content for troubleshooting.
Before starting the troubleshooting process, it is helpful to have a basic understanding of how HMR works:
- The browser establishes a WebSocket connection with the development server for real-time communication.
- Whenever the development server finishes recompiling, it sends a notification to the browser via the WebSocket. The browser then sends a
hot-update.xxxrequest to the development server to load the newly compiled module. - After receiving the new module, if it is a React project, React Refresh, an official React tool, is used to update React components. Other frameworks have similar tools.
After understanding the principle of HMR, you can follow these steps for basic troubleshooting:
1. Check the WebSocket Connection
Open the browser console and check for the presence of the [HMR] connected. log.
- If it is present, the WebSocket connection is working correctly. You can continue with the following steps.
- If it is not present, open the Network panel in Chrome and check the status of the
ws://[host]:[port]/webpack-hmrrequest. If the request is failed, this indicates that the HMR failed because the WebSocket connection was not successfully established.
There can be various reasons why the WebSocket connection fails to establish, such as using a network proxy that prevents the WebSocket request from reaching the development server. You can check whether the WebSocket request address matches your development server address. If it does not match, you can configure the WebSocket request address using tools.devServer.client.
2. Check the hot-update Requests
When you modify the code of a module and trigger a recompilation, the browser sends several hot-update.json and hot-update.js requests to the development server to fetch the updated code.
You can try modifying a module and inspect the content of the hot-update.xxx requests. If the content of the request is the latest code, it indicates that the hot update request is working correctly.
If the content of the request is incorrect, it is likely due to a network proxy. Check whether the address of the hot-update.xxx request matches your development server address. If it does not match, you need to adjust the proxy rules to route the hot-update.xxx request to the development server address.
3. Check for Other Causes
If the above two steps do not reveal any issues, it is possible that other factors are causing the HMR to fail. For example, it could be that the code does not meet React's requirements for HMR. You can refer to the following questions for further troubleshooting.
HMR not working when external React?
To ensure that HMR works properly, we need to use the development builds of React and ReactDOM.
If you exclude React via externals when bundling, the production build of React is usually injected through CDN, and this can cause HMR to fail.
To solve this problem, you need to reference the development builds of React or not configure externals in the development environment.
If you are unsure about the type of React build you are using, you can refer to the React documentation - Use the Production Build.
HMR not working when setting filename hash in development mode?
Usually, we only set the filename hash in the production mode (i.e., when process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production').
If you set the filename hash in the development mode, it may cause HMR to fail (especially for CSS files). This is because every time the file content changes, the hash value changes, preventing tools like mini-css-extract-plugin from reading the latest file content.
- Correct usage:
- Incorrect usage:
HMR not working when updating React components?
Modern.js uses React's official Fast Refresh capability to perform component hot updates.
If there is a problem that the hot update of the React component cannot take effect, or the state of the React component is lost after the hot update, it is usually because your React component uses an anonymous function. In the official practice of React Fast Refresh, it is required that the component cannot be an anonymous function, otherwise the state of the React component cannot be preserved after hot update.
Here are some examples of wrong usage:
The correct usage is to declare a name for each component function:
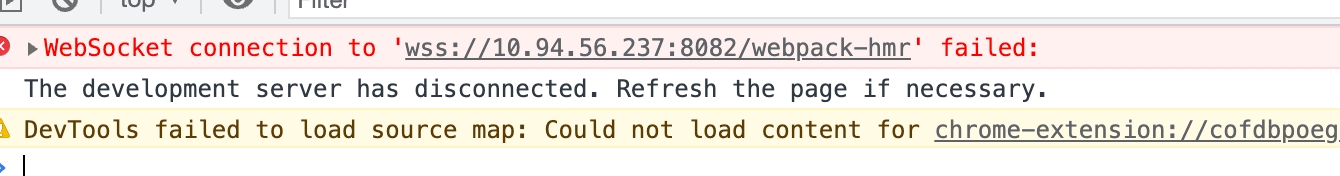
HMR not working when use https?
If https is enabled, the HMR connection may fail due to a certificate issue, and if you open the console, you will get an HMR connect failed error.
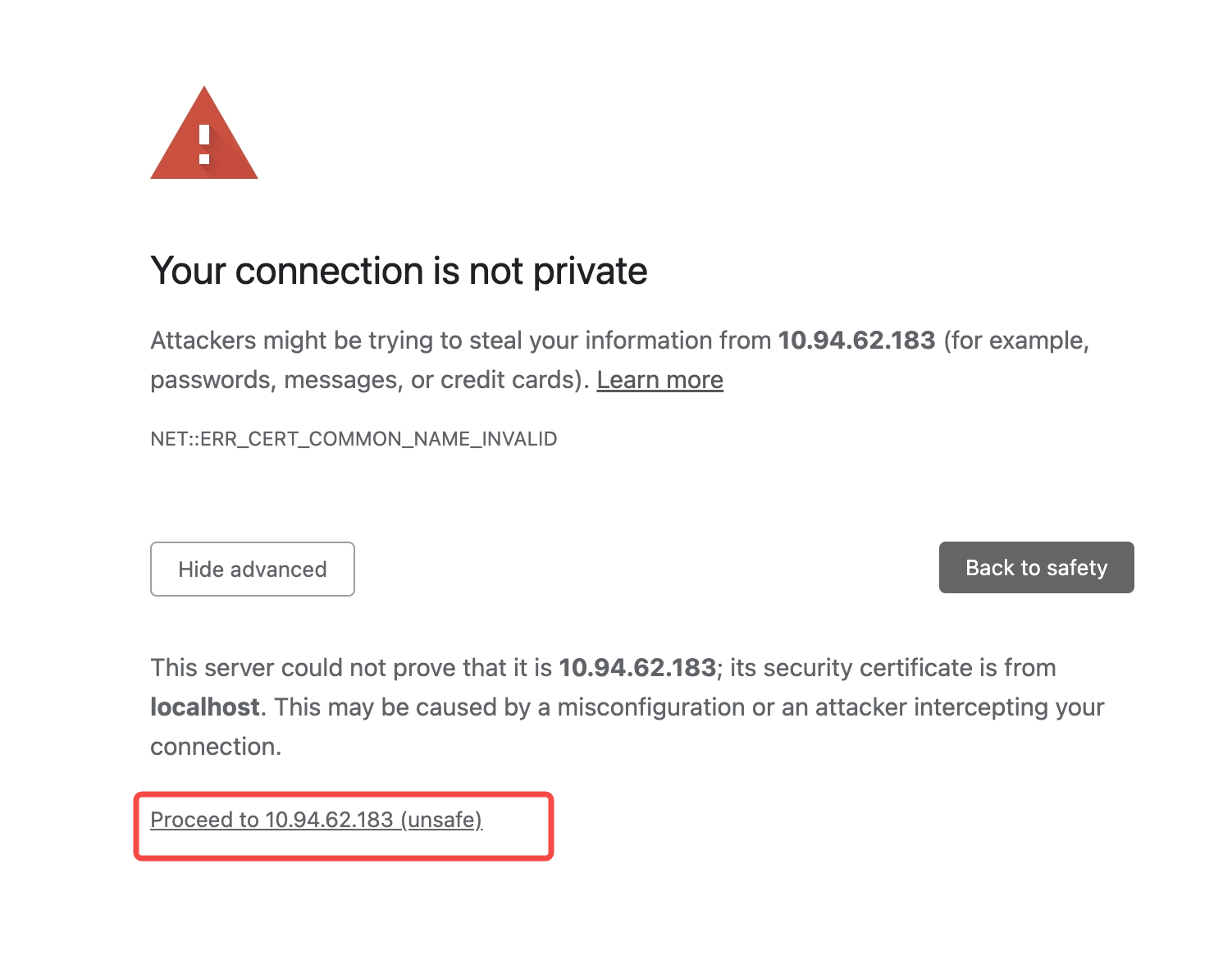
The solution to this problem is to click on "Advanced" -> "Proceed to xxx (unsafe)" on the Chrome problem page.
Tips: When accessing the page through Localhost, the words "Your connection is not private" may not appear and can be handled by visiting the Network domain.
