Data Writing
In the Data Fetching section, we introduced how Modern.js fetches data. This might bring up two questions:
- How do I update the data returned by the Data Loader?
- How do I send new data to the server?
In Modern.js, you can use Data Action to address these scenarios.
What is Data Action
Modern.js recommends managing routes using conventional routing. Each route component (layout.ts, page.ts, or $.tsx) can have a same-named .data file. These files can export an action function, known as Data Action, which developers can call at an appropriate time:
You can export a Data Action function in the routes/user/layout.data.ts file:
In the route component, you can use useFetcher to get the corresponding submit function, which executes and triggers Data Action:
After executing submit, the defined action function will be triggered. You can get the submitted data from the parameters in the action function and ultimately send the data to the server.
Once the action function executes, Modern.js will automatically run the loader function code to update the data and view accordingly.
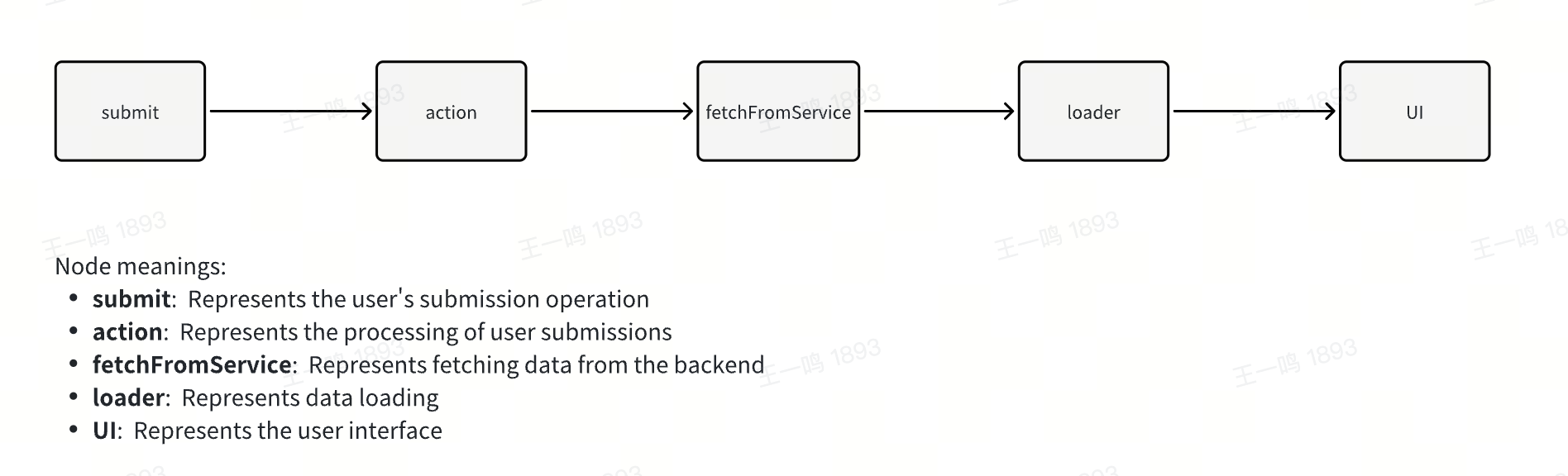
action Function
Similar to the loader function, the action function takes two parameters: params and request.
params
params is the dynamic route segments when the route is a dynamic route, which are passed as parameters to the action function:
request
request is an instance of Fetch Request.
Using request, you can retrieve data submitted from the client in the action function, such as request.json(), request.formData(), request.json(), etc. Refer to Data Types for which API to use.
Return Value
The return value of the action function can be any serializable content or a Fetch Response instance. You can access the content via useActionData.
useSubmit and useFetcher
Difference
You can call Data Action using useSubmit or useFetcher. The difference is that useSubmit triggers browser navigation, while useFetcher does not.
useSubmit:
useFetcher:
The submit function takes two parameters. The first parameter is the formData passed to the server. The second parameter is an optional object where:
methodcorresponds to the form submission method. In most data writing scenarios, you can set themethodtopost.actionspecifies the route component to trigger the Data Action. If not provided, it defaults to the current route component's action. For example, executing submit inuser/page.tsxor its sub-components will trigger the action defined inuser/page.data.ts.
More information about the API can be found in the relevant documentation: useSubmit, useFetcher.
Data Types
The first parameter of the submit function can accept different types of values.
For example, FormData:
or URLSearchParams:
or any value that the URLSearchParams constructor accepts:
By default, if the first parameter of the submit function is an object, the corresponding data will be encoded as formData:
You can also specify the encoding type via the second parameter:
or submit plain text:
Why Data Action?
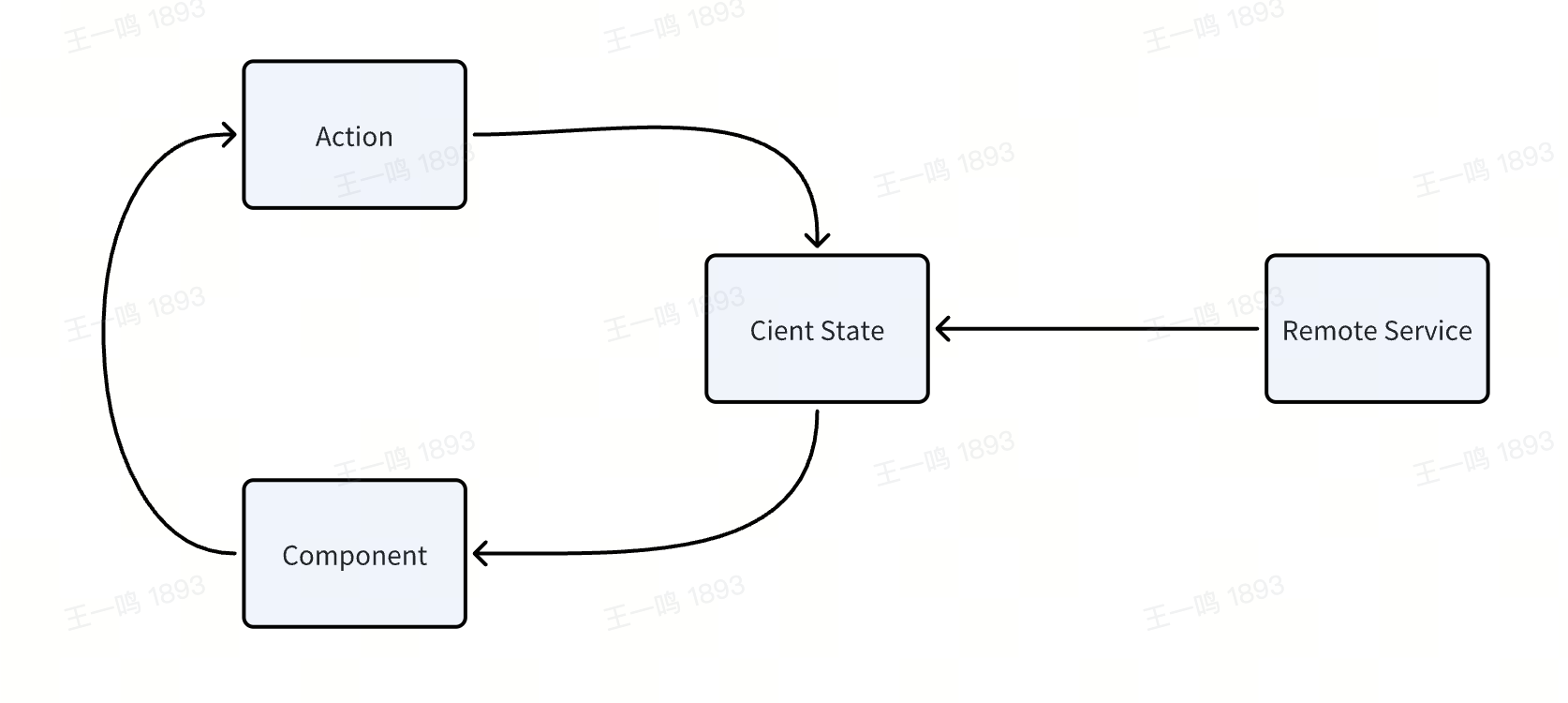
Modern.js provides Data Action primarily to keep the UI and server state in sync, reducing the burden of state management. Traditional state management methods maintain state separately on the client and remote server:
In Modern.js, we aim to help developers automatically synchronize client and server state using Loader and Action:
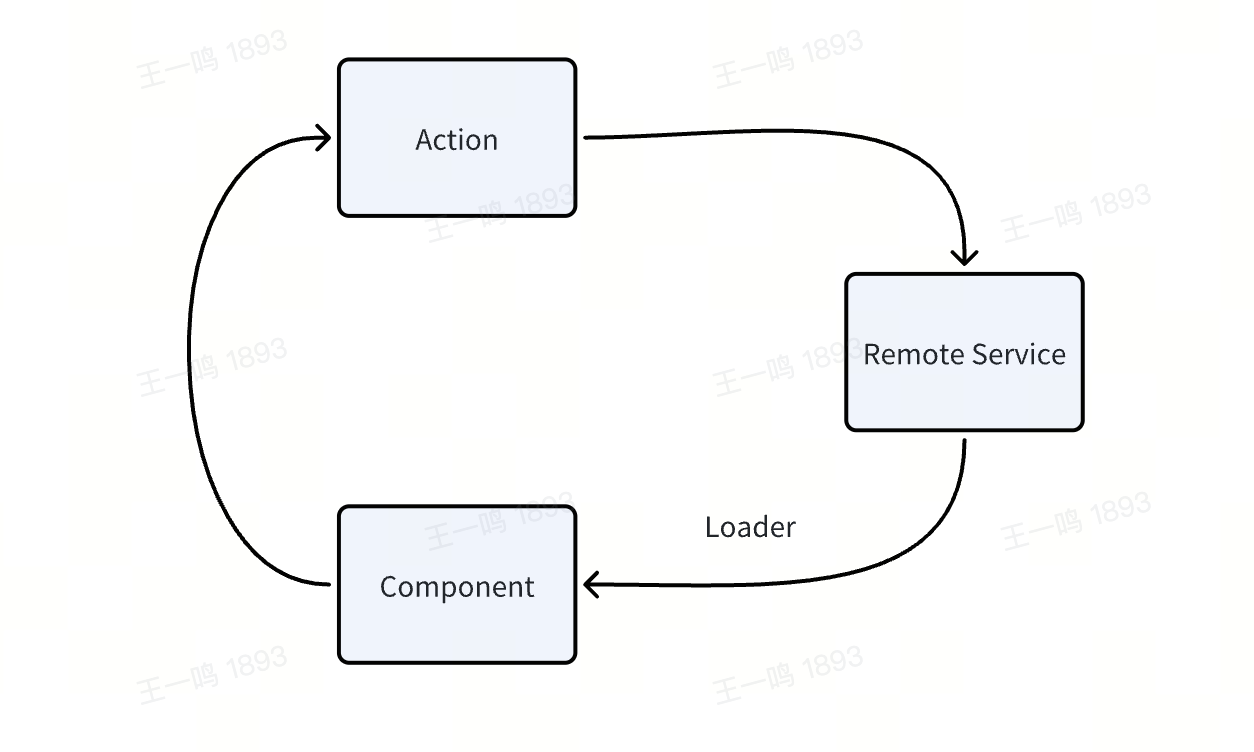
If the shared data in your project mainly comes from the server, you don't need to introduce a client-side state management library. Use Data Loader to request data and share it in sub-components via useRouteLoaderData. Use Data Action to modify and synchronize the server's state.
CSR and SSR
Similar to Data Loader, in SSR projects, Data Action is executed on the server (the framework automatically sends requests to trigger Data Action), while in CSR projects, Data Action is executed on the client.
