Extend BFF Server
In some applications, developers may want to handle all BFF functions uniformly, such as for authentication, logging, data processing, etc.
Modern.js provides two methods that allow developers to extend the BFF Server freely according to the runtime framework.
Middleware
Developers can write middleware in the api/_app.ts file to extend the BFF Server. Taking Express as the runtime framework, here is an example of how to write a middleware to add permission checks:
Then add a standard BFF function api/lambda/hello.ts:
Next, in the frontend, add the code to access the API in src/routes/page.tsx, directly using the integrated method for the call:
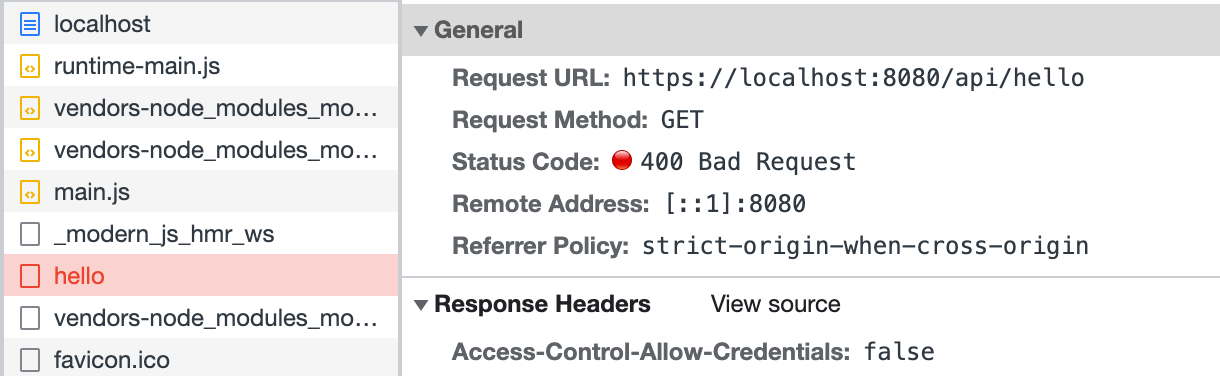
Now run the dev command to start the project, and visit http://localhost:8080/. You will find that the request to /api/hello is intercepted:
Finally, modify the frontend code in src/routes/page.tsx to call the login interface before accessing /api/hello:
Here the login interface is not actually implemented; the code is just for demonstration.
Refresh the page to see that the access to /api/hello is successful:
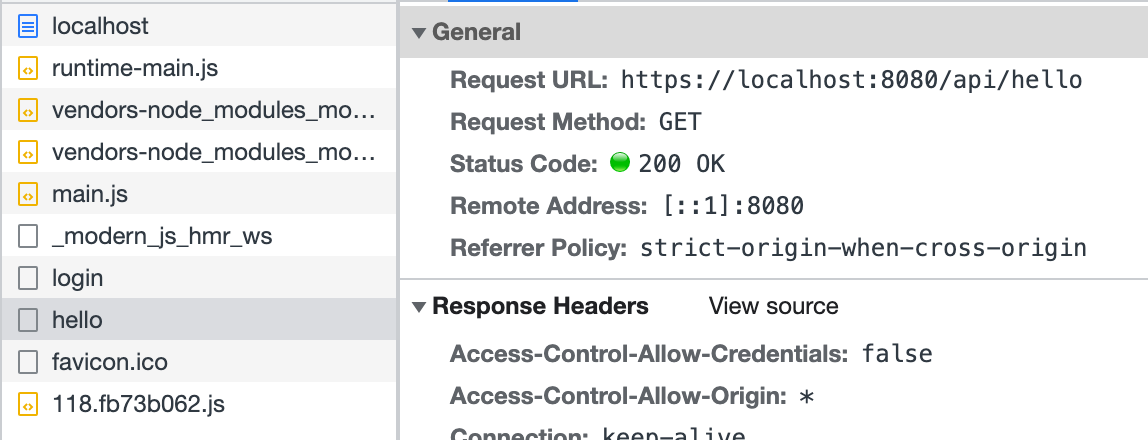
The above code simulates adding middleware in api/_app.ts to implement simple login functionality. Similarly, other functionalities can be implemented in this hook file to extend the BFF Server.
The way middleware is written may differ depending on the runtime framework. For details, see Runtime Frameworks.
Define Server Instance
In addition to middleware, you can also define a BFF Server instance via the api/app.ts. Developers need to export an instance that can be recognized by the runtime framework plugin. Here is a simple demonstration of how to define a server instance with Koa and Express.
In complex BFF logic, defining a server instance allows for easier organization of code logic and directory structure design through a single entry point. In this file, you can perform initialization logic, add global middleware, declare routes, and even extend the original framework.
The routes defined by the BFF functions will be registered after the routes defined in the app.ts file. Therefore, you can also intercept the routes defined by the BFF functions here for preprocessing or early responses.
At this time, if api/_app.ts exists in the application, the defined middleware will be executed after the middleware exported by the api/app.ts instance. In most cases, middleware can cover most customization needs for BFF functions. Only when the application's server-side logic is more complex do you need to customize the server instance.
When api/app.ts does not exist in the application, Modern.js will default to adding koa-body. When api/app.ts does exist in the application, if developers wish to use BFF functions with bodies, they will need to add koa-body themselves.
